We all know fresh air feels good, but have you ever thought about how weather conditions impact the air we breathe? It turns out, there’s a fascinating interplay between sunshine, rain, wind, and even temperature that can significantly affect air quality.
Understanding the connection between weather and air quality can help us appreciate good air days and take precautions when pollution levels rise. In this blog post, we will analyze the weather effects on air pollution and how to protect yourself from it.
Wind: The Power of Dispersion
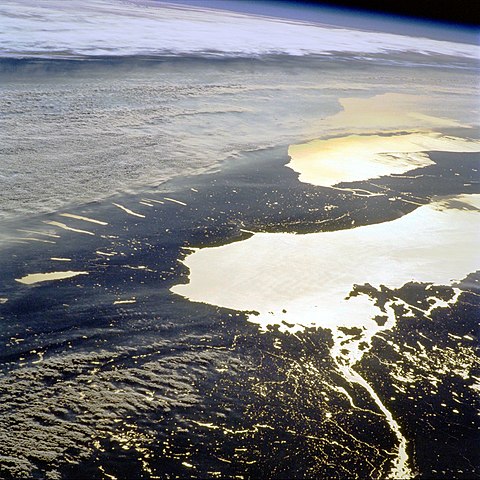
How does windy weather impact air quality? Imagine air pollution like smoke from a campfire. Calm conditions allow the smoke to linger, but a strong breeze disperses it quickly. That’s the power of wind in action. Wind speed and atmospheric turbulence play a crucial role in air quality. Strong winds physically carry air pollutants away from their source, diluting their concentration and improving air quality.
On the other hand, calm winds with stable atmospheric conditions can create a stagnant air mass. This is particularly common during winter nights when the ground cools the air near the surface. This cool, dense air gets trapped under a layer of warm air. As a result, it forms a “temperature inversion” that acts like a lid, trapping pollutants close to the ground. This can lead to poor air quality, high pollutant concentrations, and smog episodes in cities with high levels of vehicle emissions.
 Source: NASA
Source: NASA
In contrast, warm, sunny days often have good air quality due to another weather phenomenon – convection. As the sun heats the ground, the air near the surface warms and rises. This creates a vertical circulation that carries pollutants upwards, dispersing them into the atmosphere. This is why air quality often improves during the afternoon as compared to calm mornings.
Rain: Nature’s Air Scrubber
Rain is a natural air purifier. Water droplets act like tiny sponges, literally scrubbing pollutants out of the air as they fall. This is especially effective for water-soluble pollutants and particulate matter. Raindrops incorporate them and carry them to the ground.
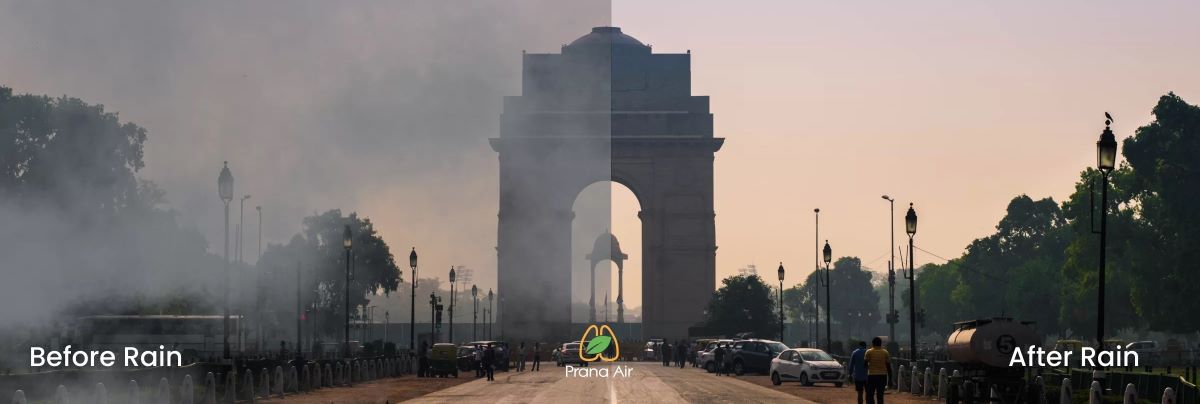

However, rain can also have a two-sided effect. Heavy rainfall can sometimes lead to pollutants being washed off surfaces and flushed into waterways, potentially causing water quality issues. Additionally, if there’s a significant amount of dust or pollen, a light drizzle might only temporarily suppress them.
Sunshine: A Double-Edged Sword
Sunshine plays a complex role in air quality. While it promotes convection, thus improving air dispersal, it can also trigger the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog. Ozone forms when sunlight reacts with nitrogen dioxide, a pollutant commonly emitted from vehicles and industrial processes. This is why smog episodes are often more prevalent during sunny days in warm weather.
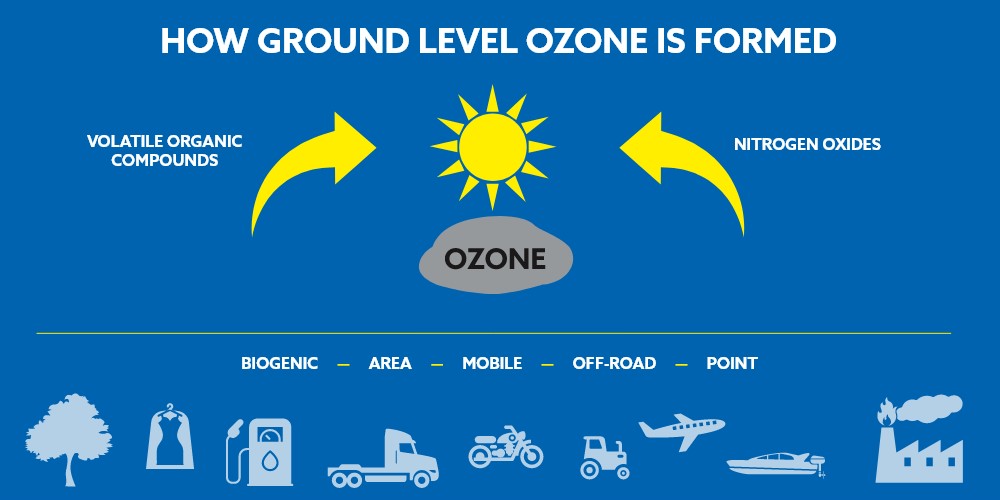 Source: Ozone Transport Commission
Source: Ozone Transport Commission
However, sunlight can also be beneficial for breaking down certain pollutants. For example, sunlight helps degrade volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from paints and solvents. So, while sunshine can create ozone, it can also help remove other pollutants under certain conditions.
The Influence of Air Temperature: Hot and Cold Effects
Temperature also plays a part in air quality. Higher temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions in the atmosphere, leading to an increase in ozone formation. This is why smog episodes are more common during hot summer months.
Cold temperatures can also have negative consequences. Cold air is denser and traps pollutants closer to the ground, similar to a temperature inversion. Additionally, colder temperatures can lead to increased emissions from vehicles because of less efficient engine combustion during cold starts.
How Do Local Weather Conditions Affect Air Quality?
The specific ways in which air quality and weather influence each other can vary depending on location. Local factors like topography, prevailing wind patterns, and types of pollution sources all play a role. For example, coastal regions might experience better air quality due to the cleansing effect of sea breezes.
Knowing your local air quality index (AQI) is a great way to stay informed. By understanding how meteorological conditions affect your local air quality, you can make informed decisions about your outdoor activities and take precautions when necessary. For example, here are the AQI standards for the United States:
| AQI | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0-50 | Good |
| 51-100 | Moderate |
| 101-150 | Unhealthy for sensitive groups |
| 151-200 | Unhealthy |
| 201-300 | Very unhealthy |
| 301+ | Hazardous |
Tips for Protecting Yourself from Air Pollution
Even when the weather isn’t cooperating, there are ways to protect yourself from polluted air:
- Limit outdoor activities. On high pollution days, consider reducing your time outdoors, especially during peak pollution hours, which often occur in the early morning or evening.
- Plan your commute. If possible, choose alternative modes of transportation like cycling, walking, or using public transit to reduce traffic emissions.
- Invest in air purifiers. These devices can help remove pollutants from indoor air. This is especially beneficial for people with respiratory problems.
- Stay informed. Monitor your local AQI in the Rain Viewer app and adjust your activities accordingly.
By working together, we can minimize the negative impact of weather on air quality and create a healthier future for ourselves and the planet. Remember, even small changes in our daily routines can contribute to cleaner air for everyone.






