Volcanic eruptions are one of the most awe-inspiring and destructive weather phenomena on Earth. These fiery spectacles not only transform the landscape but also leave a lasting mark on the planet’s weather patterns.
While we often associate volcanic eruptions with immediate local impacts, their effects can reverberate across the globe, influencing climate, temperatures, and precipitation. In this blog post, we’ll explore the impact of volcanoes on weather worldwide.
The Volcanic Catalyst
Volcanic eruptions release a mix of gases, ash, and volcanic aerosols into the atmosphere. Among these emissions, sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a key player in the volcanic weather connection. When SO2 is injected high into the stratosphere, it undergoes chemical reactions and forms sulfate aerosols. These tiny particles have a unique ability to scatter and reflect sunlight, and they can linger in the atmosphere for months to years.
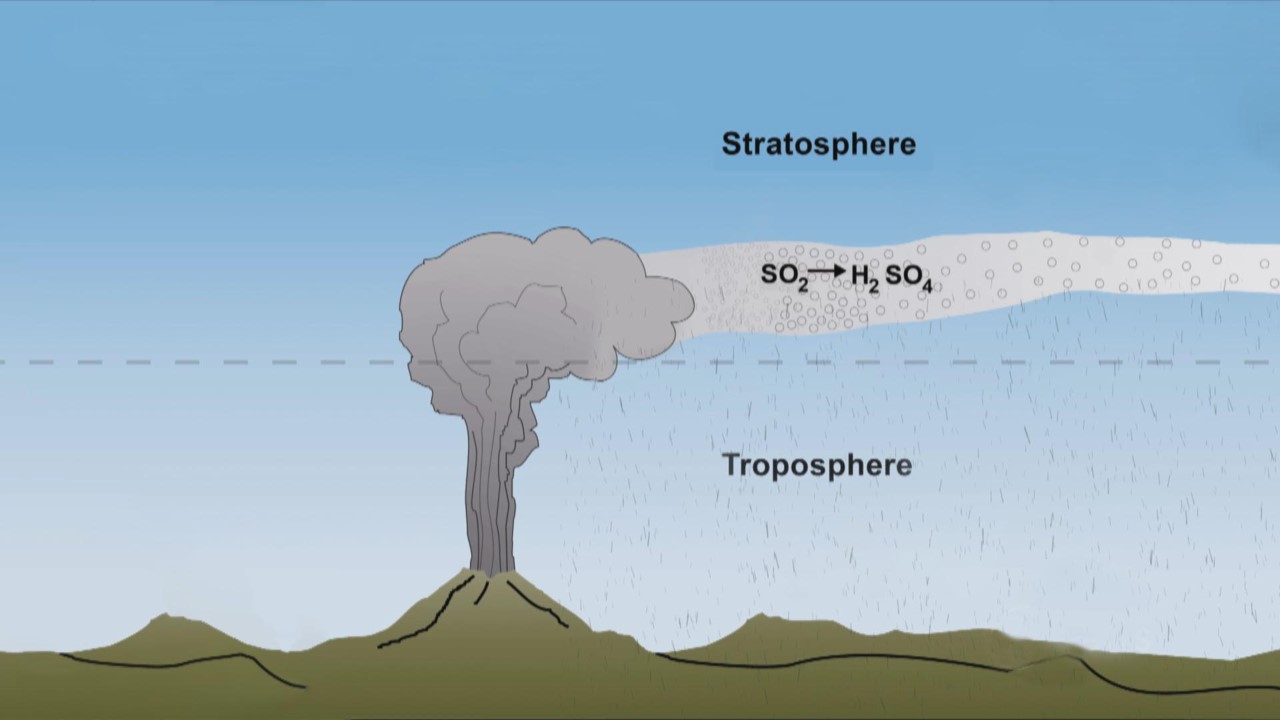 Image source: 1News
Image source: 1News
The immediate effects of a volcanic eruption are as follows:
- Volcanic ash clouds. One of the most immediate and visible effects of a volcanic eruption is the formation of massive ash clouds. These clouds can rise high into the atmosphere and, depending on the wind patterns, spread over vast areas. Ash clouds can disrupt air travel, affect visibility, and even lead to respiratory problems for those exposed to the ash.
- Pyroclastic flows. These superheated clouds of gas, ash, and rocks can race down the slopes of a volcano, causing devastation in their path.
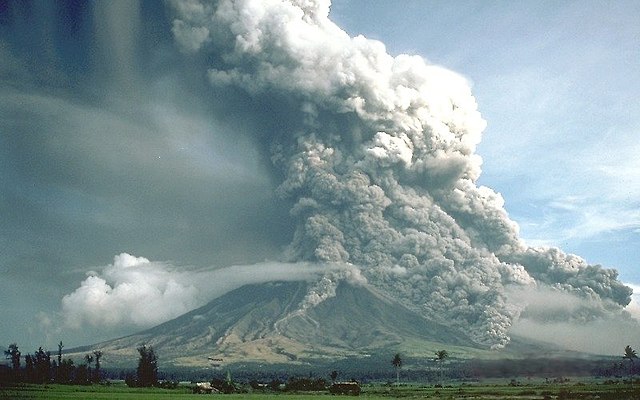 Image source: Wikipedia
Image source: Wikipedia
Here are the world’s top 5 most devastating volcanic eruptions that shaped human history:
| Eruption | Impact |
|---|---|
| Mount Tambora, Indonesia, 1815 | Cooled Earth’s temperature by nearly 5.4°F (-14°C) and caused famine in surrounding areas |
| Krakatoa, Indonesia, 1883 | Generated tsunamis, one reaching 120 feet (36 meters) high, causing around 36,000 deaths |
| Mount Vesuvius, Italy, 79 A.D. | Buried Pompeii and Herculaneum in ash |
| Mount Pinatubo, Philippines, 1991 | Forced 100,000 people to leave their homes |
| Yellowstone, U.S., 640,000+ years ago | Ash from eruptions covered much of the western half of North America |
Volcanic Eruptions: Cooling Effect on Global Temperatures
When you think of a volcanic eruption, you may associate it with heat and high temperatures. But in fact, one of the most significant consequences of volcanic eruptions is their cooling effect on global temperatures. The sulfate aerosols released during eruptions reflect sunlight into space, reducing the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface. This causes a temporary drop in temperature, often referred to as “volcanic winter” or “volcanic cooling.”
Historical records reveal that some of the most dramatic cooling events in Earth’s history were triggered by volcanic eruptions. The eruption of Mount Tambora in 1815, for example, led to the infamous “Year Without a Summer”, resulting in widespread crop failures and food shortages.
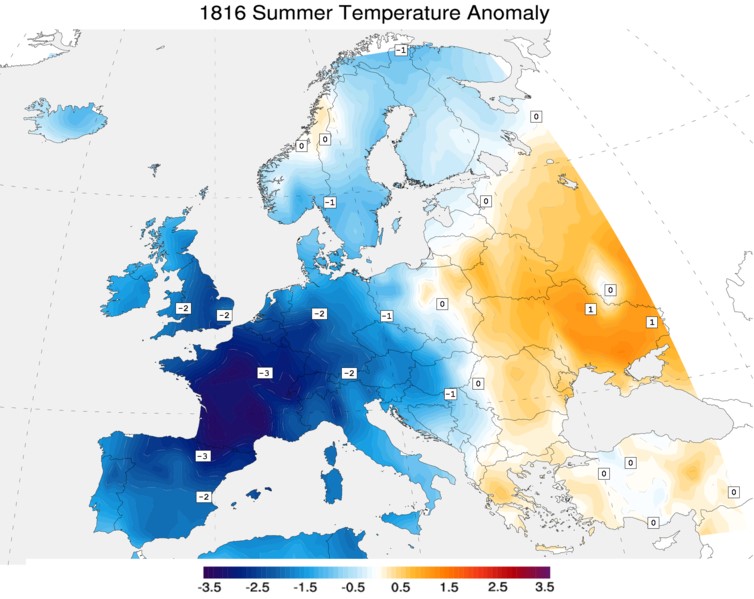 Image source: Giorgiogp2, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Image source: Giorgiogp2, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
How Volcanic Eruptions Impact Precipitation
Eruptions can have a significant impact on precipitation patterns in various ways. Here are some key details on how volcanic eruptions influence rainfall and precipitation:
Atmospheric Circulation Disruption
As we’ve already mentioned, volcanic eruptions release large quantities of sulfur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere. The resulting sulfate aerosols can scatter and reflect sunlight, leading to a temporary cooling of the Earth’s surface.
The cooling effect disrupts normal atmospheric circulation patterns. It means that big air pressure systems, such as jet streams, can change their place and strength. Changes in the position and strength of jet streams can lead to shifts in the paths of storm systems and weather fronts. This, in turn, can affect where and when rainfall occurs.
Changes in Temperature Gradients
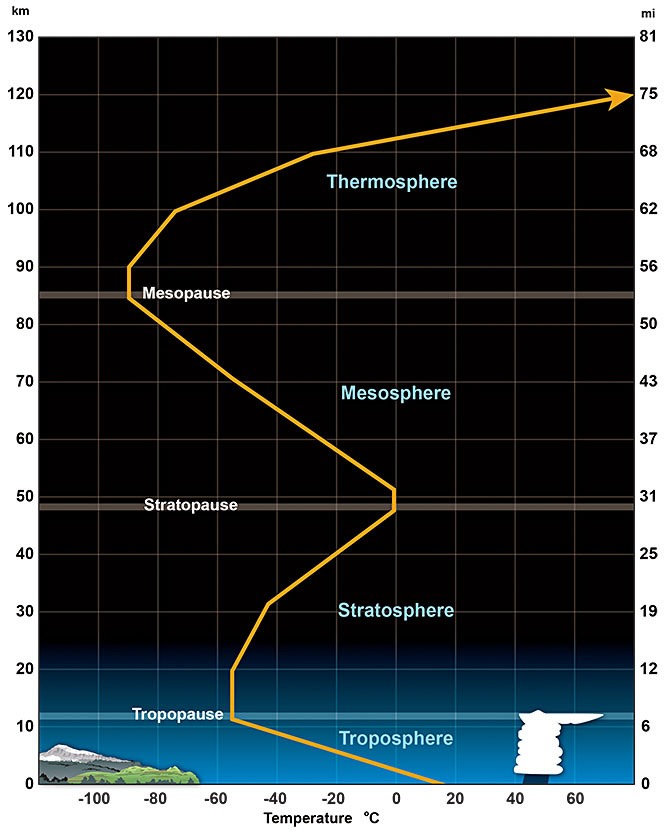 Image source: NOAA
Image source: NOAA
The cooling induced by volcanic aerosols can create temperature gradients in the atmosphere. Temperature gradients are differences in temperature between atmospheric layers that can influence the movement and behavior of air masses.
The altered temperature gradients can result in atmospheric instability, which can affect cloud formation and precipitation. In some cases, they may inhibit the development of rain clouds, resulting in drier conditions in specific regions.
Volcanic Influence on Monsoons
Monsoons are large-scale wind patterns that bring seasonal rainfall to many parts of the world, including South Asia and parts of Africa and the Americas. Volcanic eruptions can disrupt monsoon patterns.
The cooling effect of volcanic aerosols can weaken monsoon circulation by altering the temperature and pressure gradients in the region. This can lead to delayed or reduced monsoon rainfall, affecting agriculture and water resources.
Volcanic Impact on Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones, also known as hurricanes or typhoons, are massive weather systems that can wreak havoc when they make landfall. Interestingly, volcanic eruptions can influence the behavior and intensity of these storms.
Tropical cyclones thrive in an environment with high atmospheric instability. When the atmosphere is unstable, the warm, moist air rises more easily, leading to the development of strong updrafts and thunderstorms that are characteristic of cyclones.
Volcanic eruptions can temporarily stabilize the atmosphere due to the cooling effect of volcanic aerosols. This stabilization can hinder the development of the convective processes necessary for tropical cyclone formation and intensification.
Conclusion
Volcanic eruptions are not isolated events with localized consequences; they have the potential to reshape weather patterns on a global scale. Through the injection of sulfur dioxide and other emissions into the atmosphere, volcanoes can cause temporary cooling, change precipitation patterns, and influence tropical cyclones. As scientists continue to study and monitor volcanic activity, they gain valuable insights into how these powerful geological events can influence our planet’s climate.






