Agriculture is the backbone of human civilization. For millennia, farmers have relied on weather patterns to cultivate crops and raise livestock. However, this dependence makes agriculture incredibly vulnerable to weather changes. From scorching droughts to unexpected frosts, extreme weather events can affect crop yields, livestock health, and ultimately, our food security.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the various aspects of weather impact on agriculture. We’ll explore specific weather events like droughts, floods, hailstorms, and frosts, discussing their effects on different agricultural practices. We’ll also discuss strategies that farmers use to mitigate the impact of weather on crop production.
Weather and Agriculture: The Delicate Balance
Successful agriculture relies on a complex interplay between various weather factors. Here are some key elements that influence crop growth and livestock health:
Temperature
How does temperature affect crop production and growth? Different crops have specific temperature requirements for optimal growth. Excessive heat can stress plants, reduce yields, and even lead to crop failure. Conversely, prolonged cold periods can stunt growth, damage fruits and vegetables, and limit planting opportunities.
Sunlight
Plants require sunlight for photosynthesis, the process by which they convert the energy of light into food. Reduced sunlight due to excessive cloud cover or long nights can hinder growth and development.
Precipitation
How does precipitation impact agriculture? Water is essential for plant growth. However, the amount and timing of precipitation are crucial. Droughts deprive crops of much-needed moisture, while excessive rainfall can lead to waterlogging, soil erosion, and the spread of plant diseases.
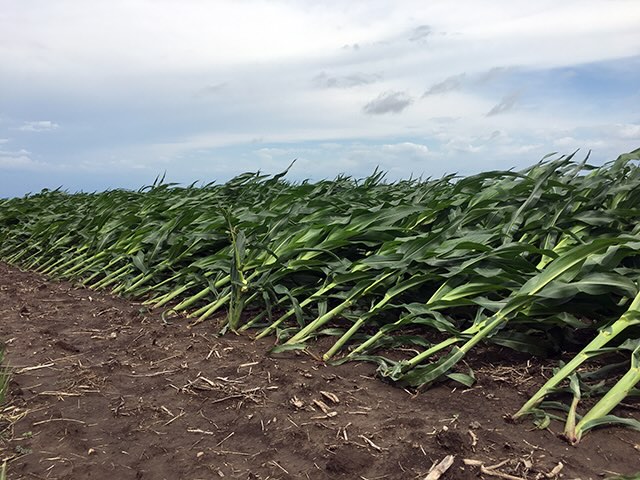
Wind
Wind can play a beneficial role by promoting pollination and helping disperse seeds. However, strong winds can damage crops, especially young seedlings, and increase soil erosion.
 Source: Pamela Smith, DTN
Source: Pamela Smith, DTN
Disruptive Forces: How Severe Weather Events Impact Farms
Now, let’s take a look at specific extreme weather events and how they disrupt agricultural activities:
Droughts
It’s impossible to underestimate the drought impact on agriculture. Droughts occur when a region experiences below-average rainfall for an extended period. This lack of moisture can have a devastating impact on agriculture. Crops wilt and die, pastures dry up, and livestock struggle to find food and water. The effects of droughts are often compounded by high temperatures, further accelerating water loss from soil and plants.
Floods
While rain is essential for agriculture, excessive rainfall can lead to flooding. Flood impact on agriculture can result in serious consequences for food production. Floods can inundate fields, impacting crop production and reducing soil fertility. Additionally, floods can damage farm infrastructure, livestock, and stored grains.
Hailstorms
Hailstones are balls of ice that form within thunderstorms. Hailstorms can cause significant damage to crops, especially fruits, vegetables, and young seedlings. The size and density of hailstones determine the extent of the hail damage to crops.
Early/Late Frosts
Frosts occur when temperatures dip below the freezing point. Depending on the timing, frosts can be detrimental to crops. Early frosts can damage or kill newly emerged seedlings, while late frosts can harm mature crops nearing harvest.
Weather and Crop Production: Impact on Different Agricultural Practices
The impact of weather events varies depending on the type of agriculture being practiced.
- Row crops (corn, soybeans, wheat). Droughts and excessive heat can significantly reduce yields of row crops. Hailstorms can damage the physical structure of the plants, affecting yield and grain quality.
 Source: Bob Nichols, USDA/CC BY 2.0 (Flickr)
Source: Bob Nichols, USDA/CC BY 2.0 (Flickr)
- Fruits and vegetables. Frost damage to crops is a significant concern, especially for fruits and vegetables, which are particularly susceptible to such conditions. Additionally, heavy rainfall can crack fruits and vegetables, reducing their market value.
- Livestock. Droughts can limit the availability of grazing land and force farmers to rely on stored feed, increasing production costs. Heat stress can affect animal health and reduce milk production in dairy cattle.
The table below summarizes severe weather events and how they affect agriculture:
| Weather Event | Impact on Agriculture |
|---|---|
| Drought | Reduced crop yields, wilting plants, water scarcity for livestock |
| Flood | Inundated fields, destroyed crops, damaged farm infrastructure |
| Hailstorm | Physical damage to crops, reduced yield, fruit and vegetable spoilage |
| Early Frost | Damage to newly emerged seedlings |
| Late Frost | Harm to mature crops nearing harvest |
Weather Impact on Agriculture: Real-Life Examples of Disruptive Forces
Let’s explore some real-life examples of how severe weather events disrupt agricultural production, including the drought and flood impact on agriculture.
The 2012-2013 US Drought
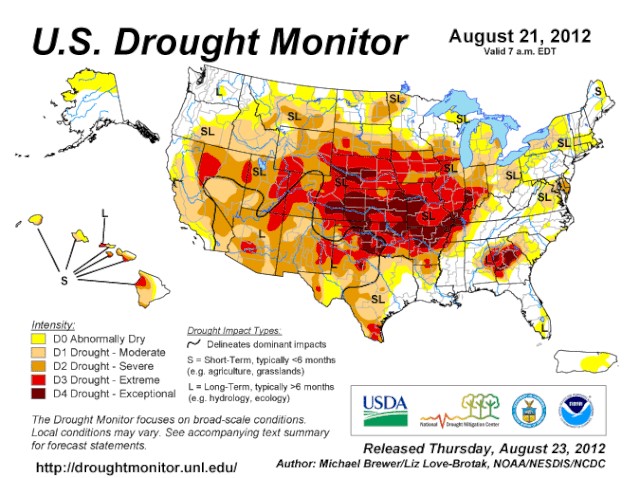 Source: Richard Heim, NOAA/NESDIS/NCDC, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Source: Richard Heim, NOAA/NESDIS/NCDC, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Having started in summer 2012, this drought lasted in the Midwest until 2013 and was one of the worst in American history. Corn and soybean yields plummeted by over 30%, sending shockwaves through global food markets and pushing food prices up significantly.
The Ongoing East African Drought
Since 2020, East Africa has been battling a devastating drought fueled by climate change. The lack of rainfall has led to widespread crop failures, leaving millions facing hunger and malnutrition.
2010 Pakistan Floods
 Source: 2010 UK Department for International Development/Russell Watkins via Flickr
Source: 2010 UK Department for International Development/Russell Watkins via Flickr
The worst floods in Pakistan’s history submerged millions of acres of farmland, destroying crops like cotton, rice, and sugarcane. Caused by heavy monsoon rains, the floods not only affected food security but also caused widespread economic damage.
2018 Iowa Floods
Heavy rains and overflowing rivers caused catastrophic flooding in Iowa, the nation’s leading producer of corn and soybeans. Millions of acres of farmland were inundated, leading to significant crop losses and economic hardship for farmers.
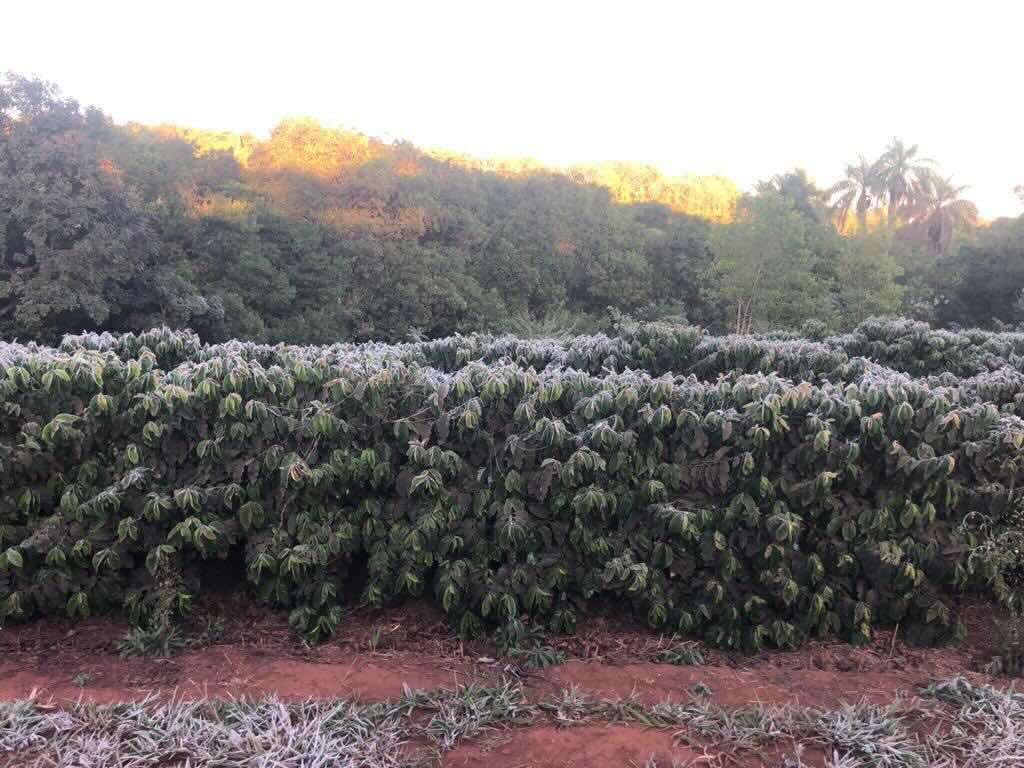
2021 Brazil Frost
 Source: Jonas Ferraresso
Source: Jonas Ferraresso
In July 2021, a series of unexpected frosts hit coffee-growing regions in Brazil, the world’s largest coffee producer. The frosts damaged coffee plants, leading to a significant drop in coffee bean production and a rise in global coffee prices.
Weather Impact Mitigation Strategies
Farmers are adopting various strategies to mitigate the impact of weather on their crops. These include:
- Planting drought-resistant crop varieties. Scientists are developing crop varieties that require less water and are more tolerant of high temperatures. For example, drought-tolerant corn varieties have deeper root systems that tap into water reserves deeper in the soil, requiring less water to grow.
- Improved irrigation practices. By using drip irrigation or precision agriculture techniques, farmers can apply water more efficiently and reduce their reliance on rainfall.
- Crop diversification. Planting a wide variety of crops with different needs helps farmers mitigate risk and secure harvests, despite adverse weather.
- Climate-smart agriculture. This approach involves using a combination of traditional and modern techniques to improve agricultural productivity while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Looking Ahead: A Data-Driven Future
Advances in weather forecasting and climate modeling can provide farmers with valuable information to make informed decisions. Real-time weather data and long-term climate projections can help farmers select appropriate crop varieties, plan planting schedules, and adjust irrigation practices to optimize yields.
By understanding how weather impacts agriculture and by adopting innovative adaptation strategies, farmers can build resilience in the face of a changing climate. This will be crucial for ensuring global food security and nourishing a growing population in the decades to come.






